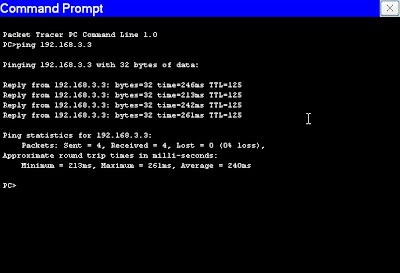
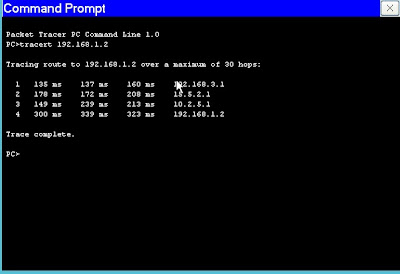
- Split horizon digunakan RIP untuk meminimalkan efek bouncing. Prinsip yang digunakan split horizon sederhana: jika node A menyampaikan datagram ke tujuan X melalui node B, maka bagi B tidak masuk akal untuk mencapai tujuan X melalui A. Jadi, A tidak perlu memberitahu B bahwa X dapat dicapai B melalui A.
- Untuk mencegah kasus menghitung-sampai-tak-hingga, RIP menggunakan metode Triggered Update. RIP memiliki timer untuk mengetahui kapan router harus kembali memberikan informasi routing. Jika terjadi perubahan pada jaringan, sementara timer belum habis, router tetap harus mengirimkan informasi routing karena dipicu oleh perubahan tersebut (triggered update). Dengan demikian, router-router di jaringan dapat dengan cepat mengetahui perubahan yang terjadi dan meminimalkan kemungkinan routing loop terjadi.
- Holddown timer adalah interval tertentu dalam detik yang berlaku untuk semua interface router yang menyatakan bahwa suatu route tidak dapat dicapai.
- poisonnus reverse, yaitu router tetap mmberikan informasi mengenai suatu router kepada sumber, tetapi memberikan nilai tidak terhingga. Dengan poisonous reverse, router-router tetap dapat mengetahui bahwa suatu jaringan ada.
RIP mempunyai default update setiap 30 detik. Disamping itu RIP juga mempunyai beberapa jenis timer lainnya yang juga
perlu diketahui sebagai berikut:
• Invalid timer adalah waktu dalam detik dimana suatu route dinyatakan tidak
berfungsi (invalid)
• Holddown timer adalah interval tertentu dalam detik yang berlaku untuk semua
interface router yang menyatakan bahwa suatu route tidak dapat dicapai.
• Flash timer adalah waktu dalam detik dimana suatu route akan dihapus dari tabel
routing.
Router A bertetangga dengan router B dan C. Terdapat router J yang berjarak
Setiap router saling bertukar catatan setiap selang waktu tertentu. Jika jumlah lompatan lebih dari 16, router akan menganggap jaraknya tak hingga dan memilih router default jika ditentukan.
Terbatasnya jumlah hop adalah salah satu kelemahan sistem RIP. Kelemahan yang lain, informasi routing disampaikan secara broadcast sehingga membebani jaringan karena host nonrouter juga dikirimi, namun sudah diperbaharui pada versi dua dengan kemampuan multicast.
Karena bentuk informasi routing yang demikian, adakalanya informasi yang disampaikan dua router tidak sama sehingga menimbulkan routing loop. Contoh routing loop, router A menganggap untuk mencapai router C adalah melewati router B, tetapi router juga menganggap untuk mencapai router C adalah melewati router A. Proses terjadinya routing loop misalnya seperti ini:
Router A, B, dan C saling bertetangga sehingga catatan pada router A dan B untuk mencapai router C:
Router A
ke C : 1
ke C lewat B : 2
Router B
ke C : 1
ke C lewat A: 2
Pada suatu saat, router C mati dan router A mengetahui lebih dahulu daripada router B sehingga catatan untuk router C pada router A dihapus. Sesudah itu terjadi pengiriman data routing dari B yang belum tahu bahwa router C mati sehingga pada router A tercatat kembali “ke C lewat B : 3 (2+1)”. Sesudah itu router B baru menyadari bahwa router C mati dan menghapus data router C namun kemudian datang info routing dari A bahwa “A ke C : 3” sehingga di B terdapat catatan “ke C lewat A : 4”. Router A kembali menyadari bahwa C mati namun kemudian mendapat informasi routing dari B sehingga catatan untuk C muncul kembali, yaitu “ke C lewat B : 5”. Hal ini kan terjadi terus menerus sampai nilai lompatan mencapai 16.
Untuk menghindari hal semacam ini, router dipaksa menyampaikan informasi routing begitu ada perubahan dan tidak menunggu waktu yang telah dijadualkan (triggered update). Selain itu juga digunakan sistem split horizon. Contoh penerapan split horizon :
Router A dan C dihubungkan oleh router B. router B menyampaikan informasi ke A bahwa jaraknya ke C adalah satu dan menyampaikan ke C bahwa jaraknya ke A adalah satu. Sehingga pada A, jarak ke C adalah dua melalui B dan pada C, jarak ke A adalah dua melalui B. Dengan split horizon, router A tidak akan menyampaikan informasi ke B mengenai router C pula dengan C, tidak akan menyampaikan informasi ke B mengenai A.